Growth Cone Phosphoproteomics Reveals that GAP-43 Phosphorylated by JNK Is a Marker of Axon Growth and Regeneration - ScienceDirect

Timeline of GAP-43, OMP, and AC3 expression. Distribution of GAP-43 +... | Download Scientific Diagram
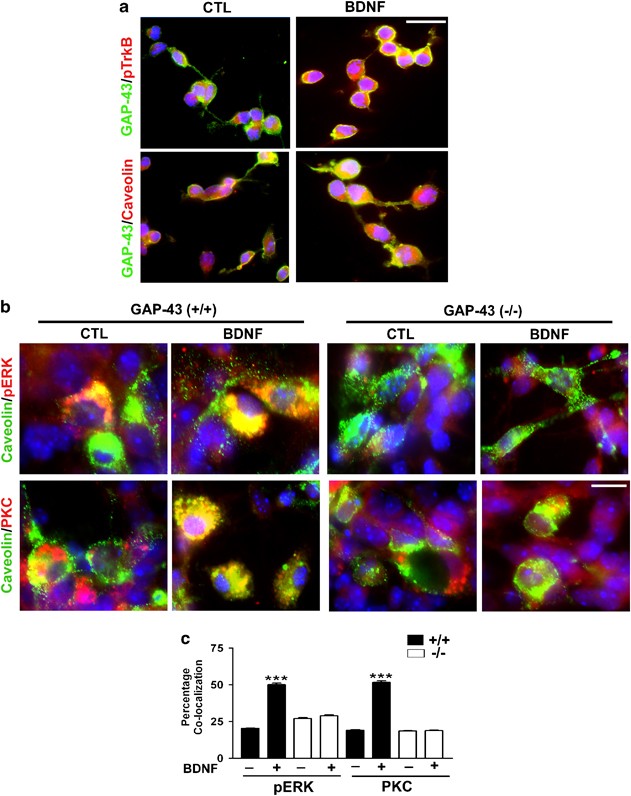
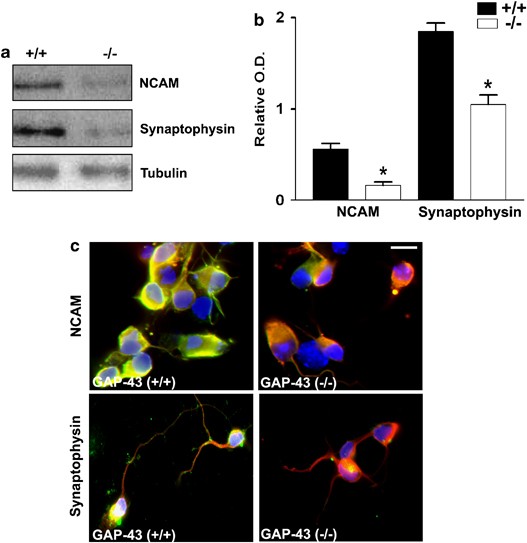
GAP-43 is essential for the neurotrophic effects of BDNF and positive AMPA receptor modulator S18986 | Cell Death & Differentiation
GAP-43 is essential for the neurotrophic effects of BDNF and positive AMPA receptor modulator S18986 | Cell Death & Differentiation

Fluid Biomarkers for Synaptic Dysfunction and Loss - Elena Camporesi, Johanna Nilsson, Ann Brinkmalm, Bruno Becker, Nicholas J Ashton, Kaj Blennow, Henrik Zetterberg, 2020
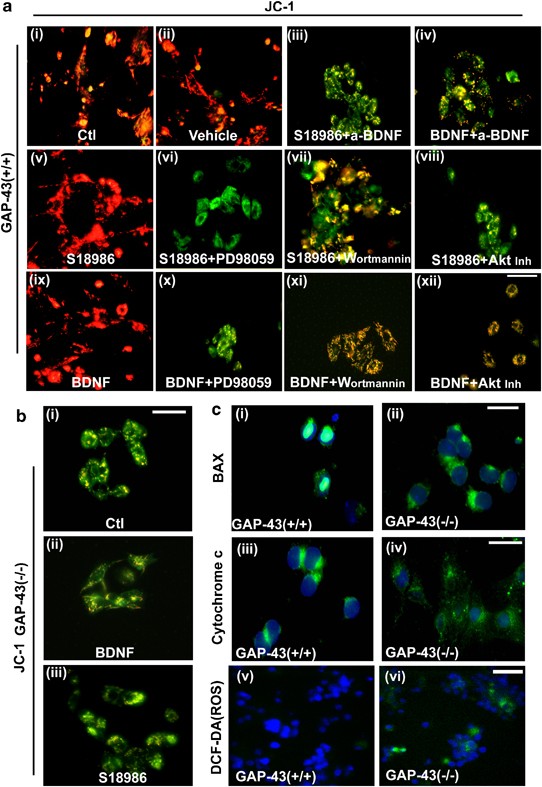
GAP-43 is essential for the neurotrophic effects of BDNF and positive AMPA receptor modulator S18986 | Cell Death & Differentiation
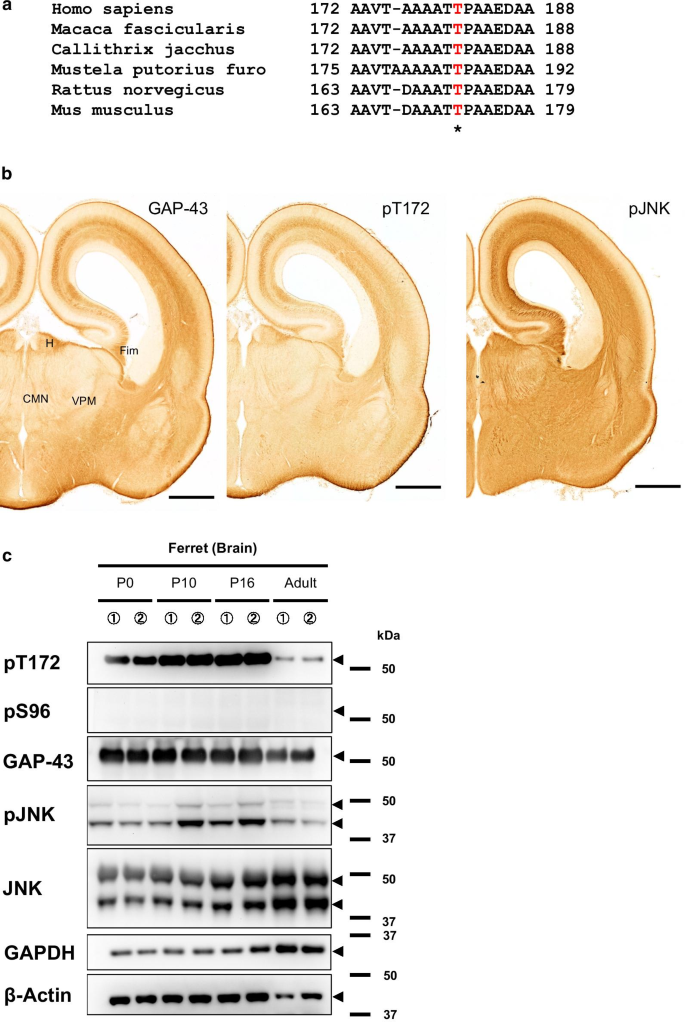
Phosphorylation of GAP-43 T172 is a molecular marker of growing axons in a wide range of mammals including primates | Molecular Brain | Full Text
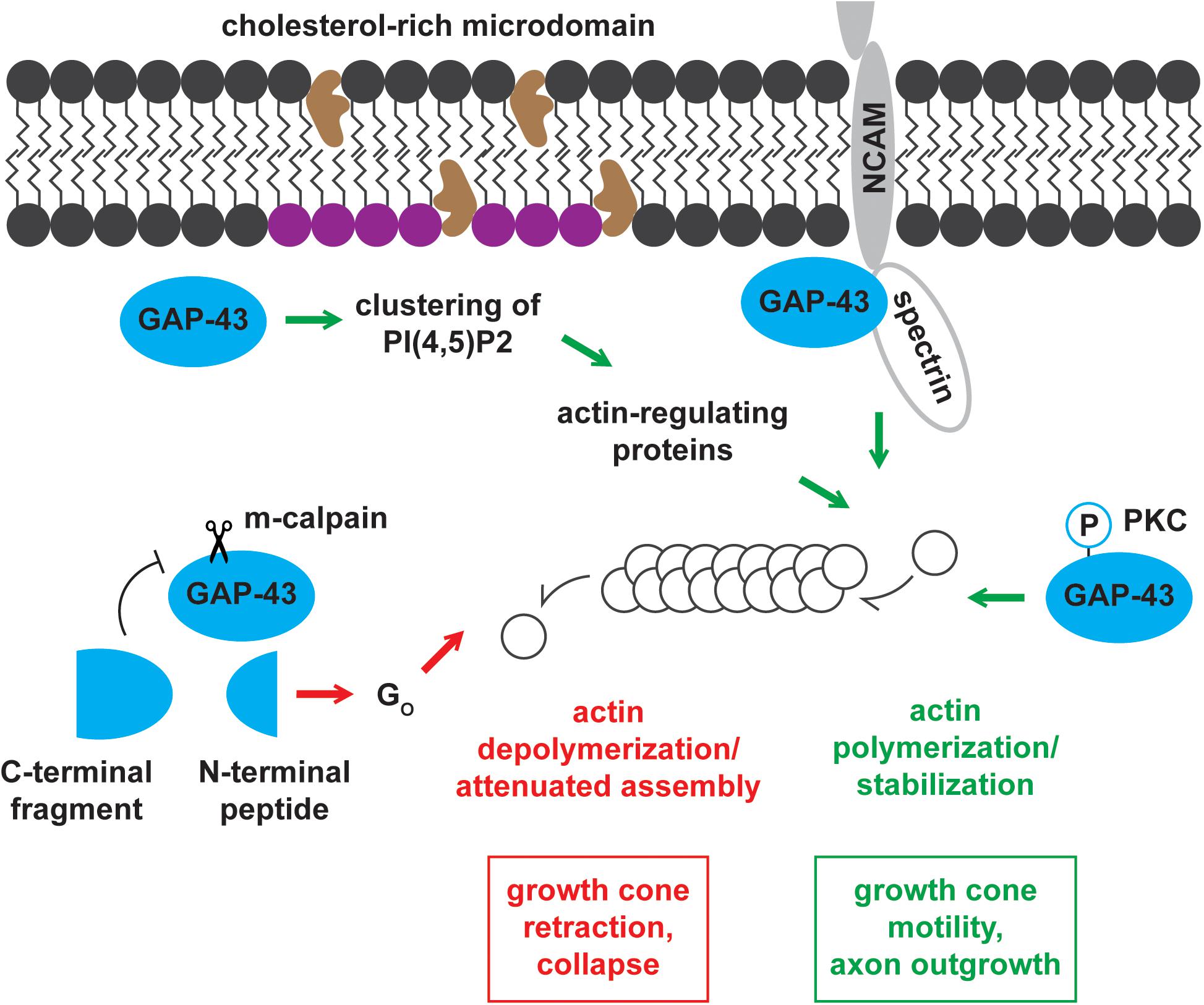
Frontiers | GAP-43 and BASP1 in Axon Regeneration: Implications for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases
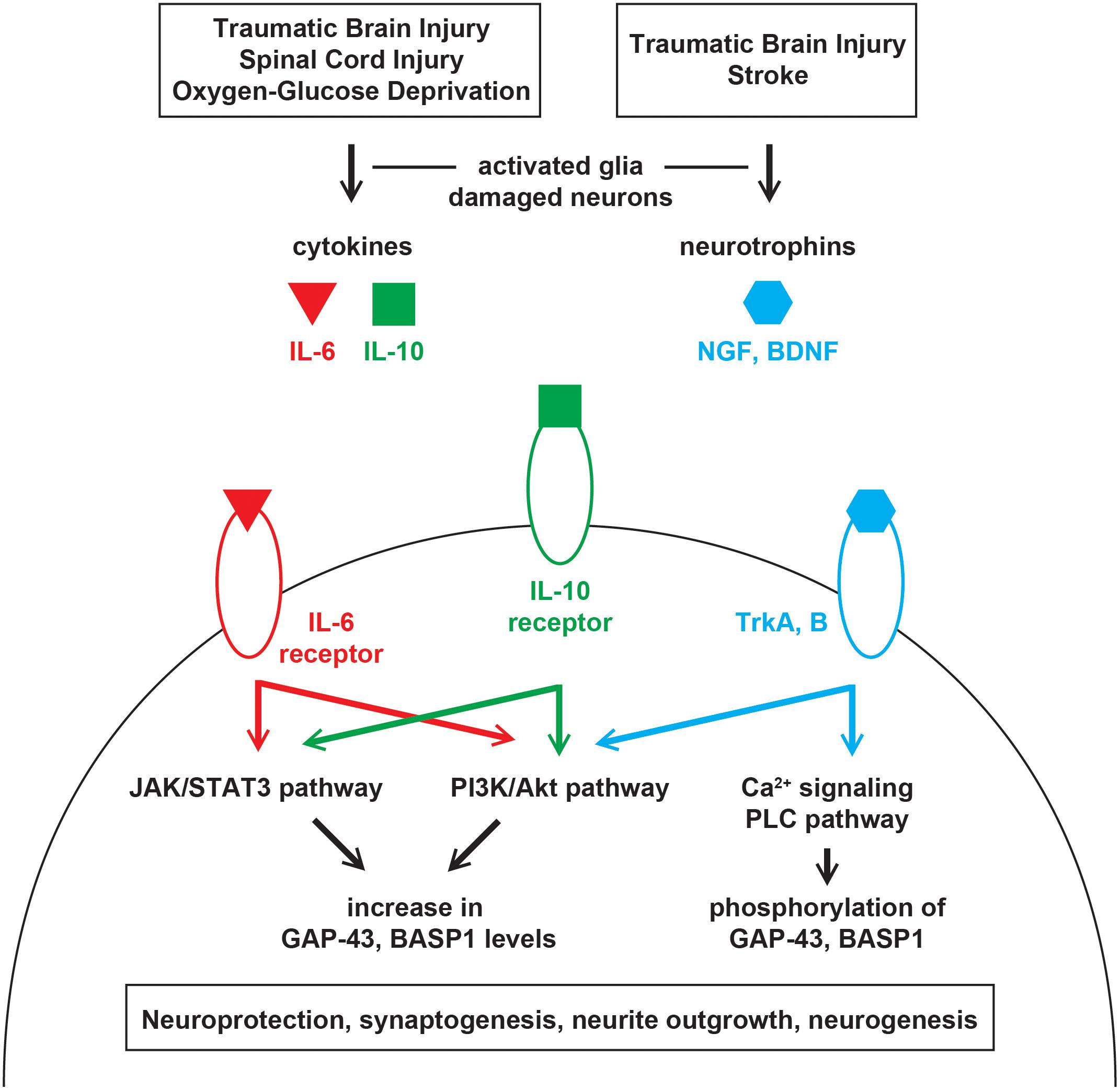
Frontiers | GAP-43 and BASP1 in Axon Regeneration: Implications for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases
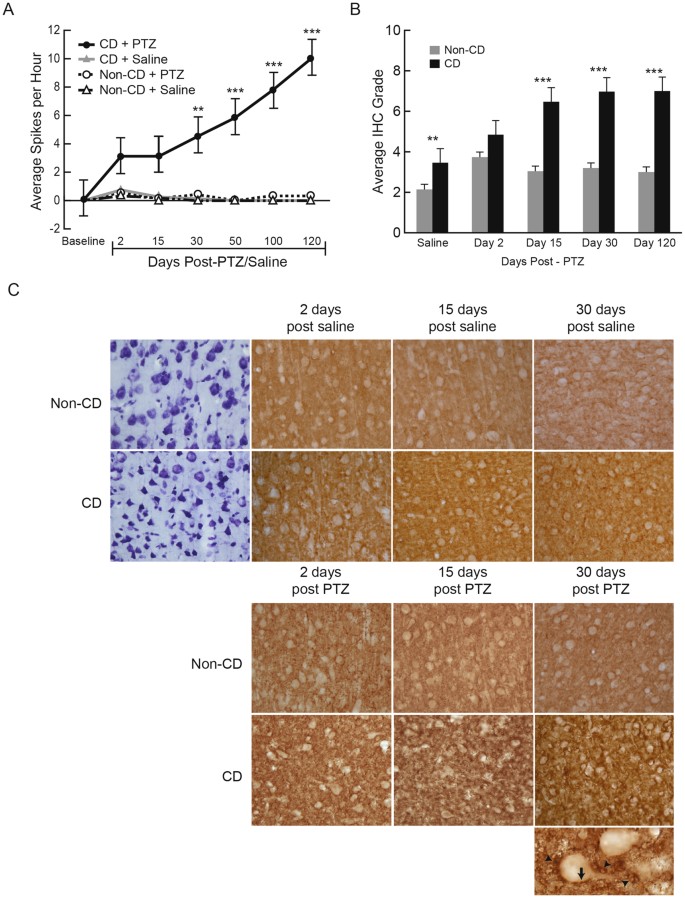
Growth Associated Protein 43 (GAP-43) as a Novel Target for the Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention of Epileptogenesis | Scientific Reports
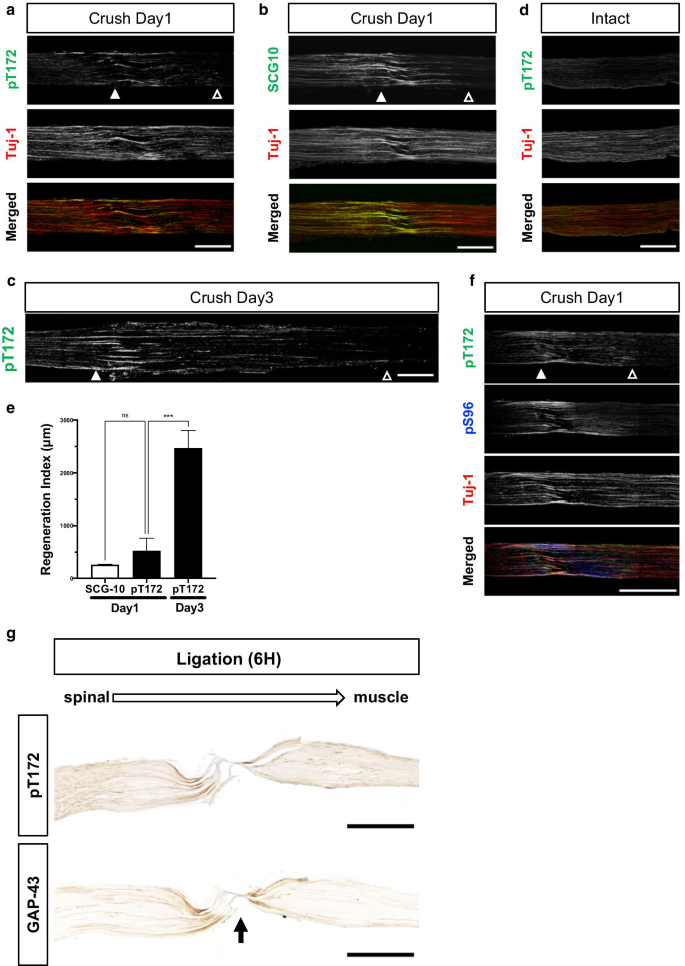
Phosphorylation of GAP-43 T172 is a molecular marker of growing axons in a wide range of mammals including primates | Molecular Brain | Full Text

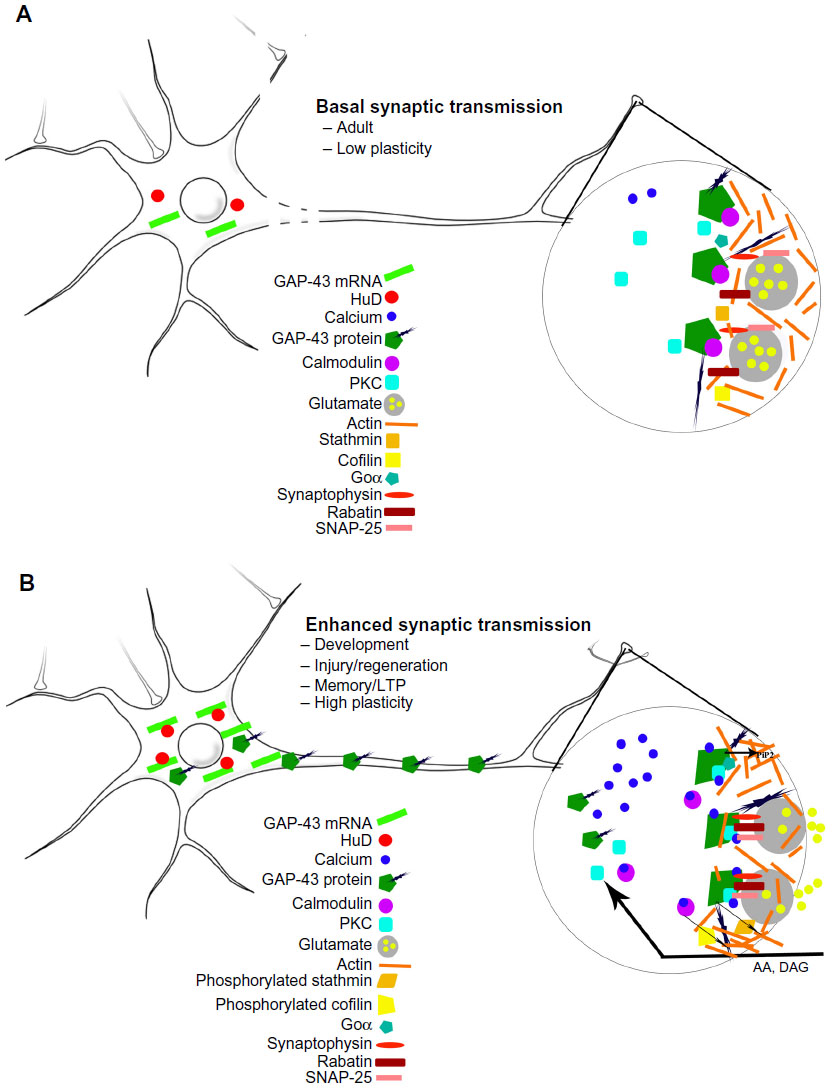
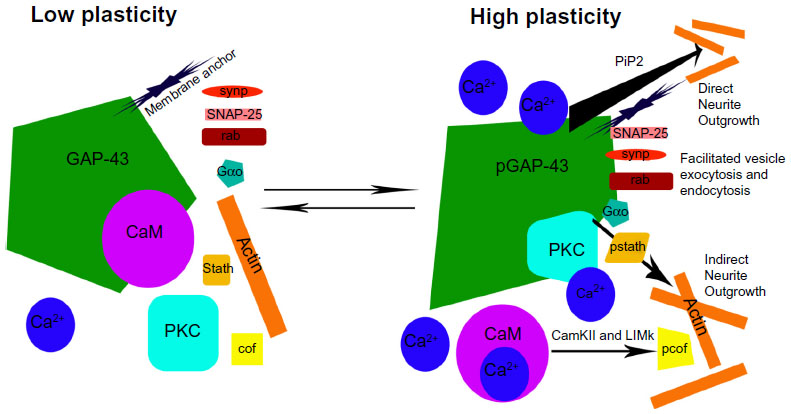
Frontiers | A Shift from a Pivotal to Supporting Role for the Growth-Associated Protein (GAP-43) in the Coordination of Axonal Structural and Functional Plasticity

The Neuronal Growth-Associated Protein GAP-43 Interacts with Rabaptin-5 and Participates in Endocytosis | Journal of Neuroscience
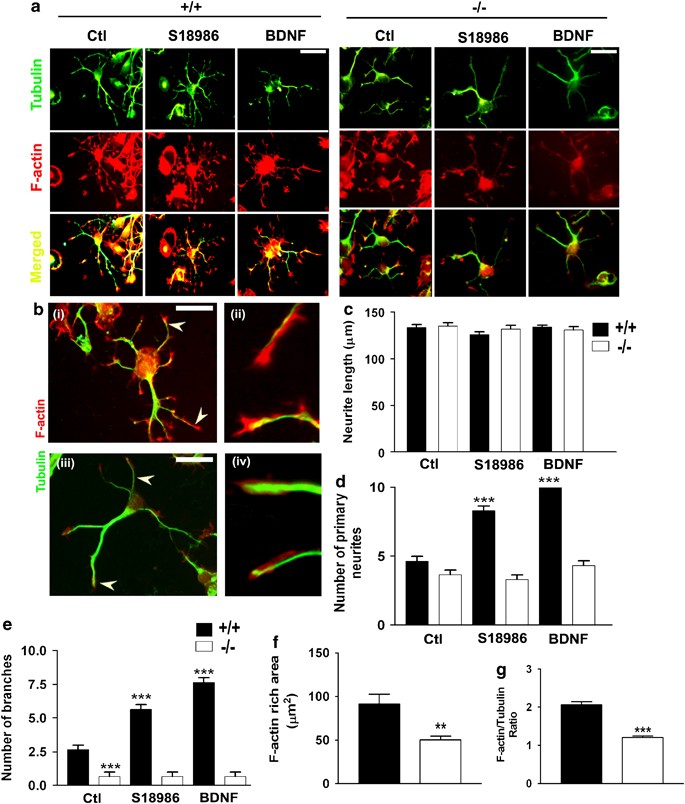
GAP-43 is essential for the neurotrophic effects of BDNF and positive AMPA receptor modulator S18986 | Cell Death & Differentiation

Growth Associated Protein 43 (GAP-43) as a Novel Target for the Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention of Epileptogenesis | Scientific Reports
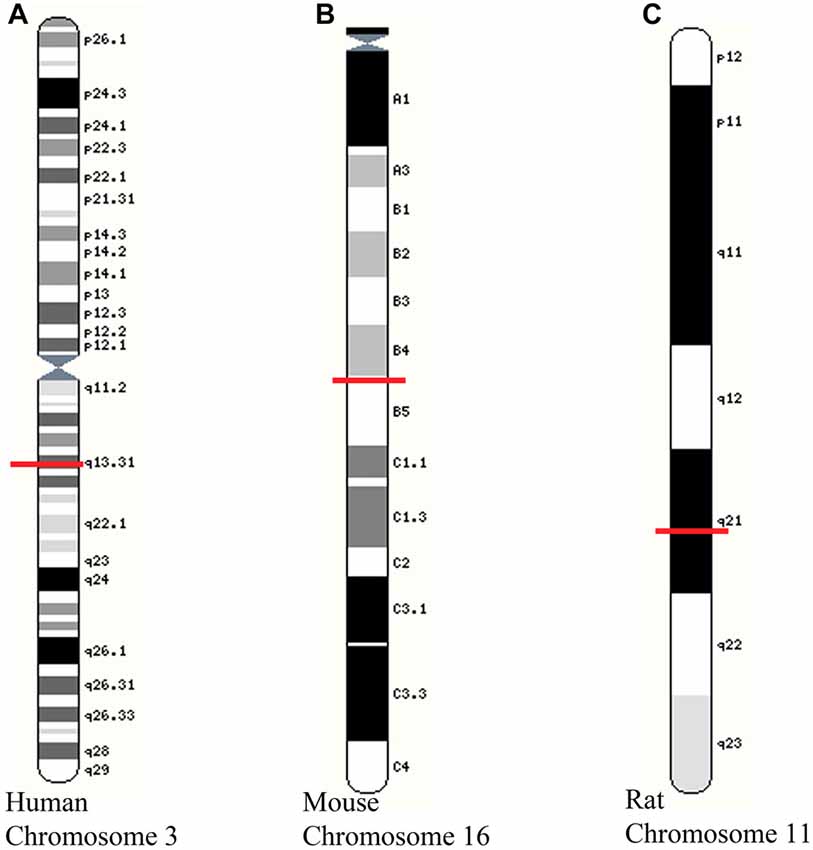
Frontiers | A Shift from a Pivotal to Supporting Role for the Growth-Associated Protein (GAP-43) in the Coordination of Axonal Structural and Functional Plasticity